Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery is a branch of science that applies the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic methods for the correction of diseases, injuries and disorders of hard and soft tissues in the mouth, teeth and jaw areas of individuals of all age ranges.

Covering treatments
Normal and surgical extraction of teeth
Embedded tooth extraction
Surgical treatment of infections in the mouth, jaw and face area
Diagnosis of cysts and tumors of the jaw and treatment of cysts
Preprothetic surgery operations
Sinus base upgrade operations
Bone augmentations
Diagnosis, treatment and long-term follow-up of traumatic dental and supporting tissue injuries
Cyst Surgery
In the case of progression of caries and gingivitis, microbes move to the root end through the root canals of the tooth or the cavity around the tooth (Periodontal December). Bacteria that reach the root tip usually lead to formations called apical abscesses or cysts here. An abscess refers to an acute condition that is more painful, and if the abscess is not treated, the inflammatory cells are organized and return to the cyst state, even if the pain subsides. Cysts in the roots of teeth are largely benign, however, if they are not treated, melts and bone loss occur in the jaw bones. In order for cysts not to form, what needs to be done is first to ensure that caries does not progress and to have their fillings and gum care done.
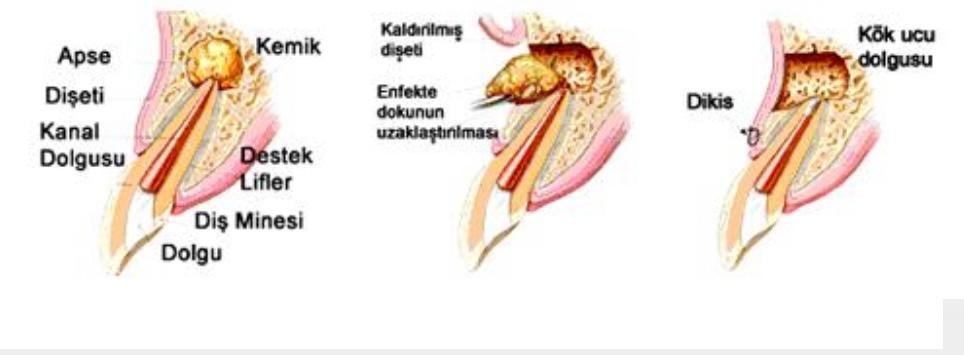
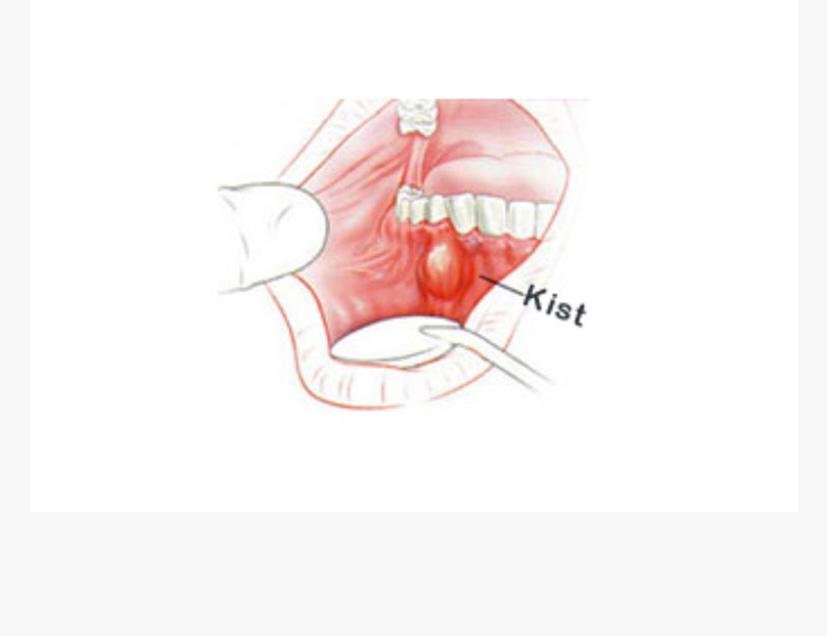
Carious teeth, even if they do not hurt, should be treated immediately when they are noticed. The treatment option that can be applied after the cyst is formed is primarily root canal treatment. If there is no result after trying canal therapy, a treatment called apical resection can be applied. In this treatment, the cyst at the level of the tooth root is reached and cleaned surgically. If necessary, bone powder is also applied to this area during the operation to accelerate healing. Apical resection is an operation that can usually be performed on the teeth in the anterior region. The opened area Decovers externally in 1 week, and the complete healing of the bone inside occurs within 2-3 months.<strong>Cyst Operations</strong> Although cysts that grow and spread quite quickly and have the shape of a sac usually have a liquid collection inside, in some cases there may also be air or solids. The first reason for the formation of a dental cyst is the lack of attention to oral hygiene. Dental cysts are formed, sometimes due to dental injuries and traumas. Jaw cysts, on the other hand, can be caused by odontogenic epithelium, as well as they can be caused by a completely different embryological origin. Although the difficulty of dental cyst surgery varies depending on the area and size of the cyst, it is not a difficult operation to be feared. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.

